Predicting Filtration Performance Using Native Particles
Date Published 2023 | Conference materials
To access our resources you will need to be a member of UltraFacility, log in to your account or purchase a membership to view this content.
In this study, we develop the technique of using a liquid particle counter to measure the retention of polymer membrane filters and apply that technique to two use cases. In the first use case, we look at the performance of two membranes in 30% hydrogen peroxide and compare the results with the retention performance measured by single nanoparticle ICP-MS and the more traditional standardized particle techniques. In the second use case, we investigate several different polymer membranes in hydrochloric acid and study the impact of pore size and surface modification on the native particle removal efficiency and compare this with traditional techniques. These two use cases demonstrate the utility of this technique and its ability to provide insight into the performance of polymer membrane filters where existing methods do not.
Related content

Deconstructing the Challenges of Facility 2.0: Device Complexity Drives Facility Complexity
Cobetter Filtration - NOVACON™
Investigation of 10 nm Particles and its Reduction Systems for UPW Production
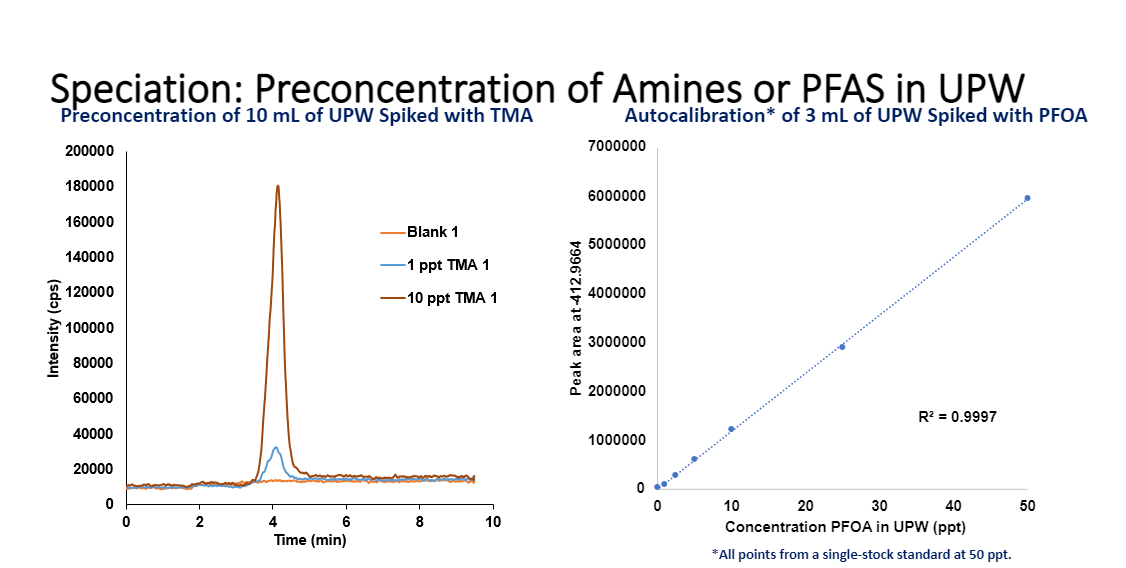
Online Automated Determination of Organic Contaminants in Semiconductor Grade Chemicals
Back to results